EHR Implementation Plan: Your 8-Step Checklist
The EHR implementation process can be a difficult time particularly due to the risks involved with getting the process wrong. As such, organizations, rightly, have many questions about implementing EHR, particularly what it entails and how to go about it in a manner that positions them best for success.
What is EHR implementation?
An EHR implementation is the process of planning and carrying out the integration of EHR software and components in a healthcare organization. Implementation is a term that is not specific to EHR systems, it refers to integrating a software-based service or component into the workflow of an organizational structure or an individual end-user. An EHR system implementation is an organization-wide effort - the impacts of which will be felt by everyone from physicians and administrative staff all the way to the patients.
How long does EHR implementation take?
How long an EHR implementation will take depends on the context. Given the number of variables that can either increase or decrease the time needed for an EHR implementation the typical time needed for implementation vary according to setting and product. As such, one cannot easily find a standard timeline for EHR implementation. However, when creating an EHR implementation plan a certain amount of the uncertainty regarding timing can be eliminated as experts involved in the process can provide solid estimates regarding the amount of time needed to complete the implementation.
What are EHR implementation steps?
Moving beyond the general roadmap or checklist provided here, it’s important to look at the steps involved in the EHR implementation process in a more detailed fashion. The EHR implementation process generally follows the following steps.
- Selection team building: selecting and organizing the individuals who will be involved in selecting the EHR.
- Requirements gathering: requirements gathering refers to the process of determining what features and functionality your practice requires in an EHR.
- RFI and RFP: once the requirements list has been created the selection team will research potential vendors and then submit Requests for Information (RFI) and Request for Proposals (RFP) to prospective vendors.
- Evaluate RFI and RFP responses: once RFIs and RFPs have been returned the selection team will evaluate these responses based on how well they adhere to the requirements list.
- Ranking of vendors to create a shortlist: the top vendor/candidates will be narrowed down to a shortlist of 3 or 4 finalists who will then be asked to provide a vendor demonstration.
- Vendor demonstrations: shortlisted vendors will conduct demonstrations of their products using presentations and simulations of their product for the selection team. The selection team will then have the opportunity to ask questions.
- Selection: a vendor is selected, contracts are negotiated and the process moves forward to actually implementing the EHR product.
- Planning and go-live preparation: with the help of the vendor the selection team and representatives from the vendor will plan out how the software and hardware will be deployed. Also, plans will be made for staff to be trained on the new system.
At this time a go-live date will be selected along with other milestones related to the deployment.
Your practice may not be ready to achieve success in these areas right now, but you and your implementation plan are going to change that using this 8-step checklist with all the stages of EHR implementation.
1. Build your EHR implementation roadmap
Roadmap. Checklist. Matrix. Template. Call it what you want.
The first stage in any EHR implementation plan is to outline all the tasks and processes which need to be executed by your team of physicians, practice managers, IT staff (and even patients). Key tasks include:
- Recruit your implementation committee from stakeholder groups
- Outline your expected implementation costs and define the total budget
- Schedule your implementation (best done after your roadmap is complete)
- Migration of patient and practice data
- Create a user training program
- EHR testing (unleashing it in a “live” practice environment at some point)
- Clearly define go-live activities
- Define critical success factors and evaluation strategies
Whether you choose to map these tasks in a checklist, roadmap or GANNT chart will depend on your practice’s project management protocols but commonly used tools include:
- Google Sheets - great for collaborating on roadmaps
- Trello or Wrike - great for flexible project management (GANNT, calendar, checklists)
- Asana - great for advanced “to-do” lists
2. Recruit your EHR implementation committee
With your implementation tasks defined you need people to execute each process on schedule and budget. The following committee members can be sourced from key stakeholder groups or external consultancy:
- Project Manager - if you’re reading this, you may have volunteered already
- Application Analyst - responsible for data migration and cleansing
- Application Developer - responsible for system customization
- QA Test Engineer - responsible for system testing and performance
- Physician Advocate - represent physicians and advise on training, data and testing
- Nurse Advocate - represent nurses and advise on training, data and testing
- Billing Advocate - represent billing department and advise on training, data and testing
- Meaningful-Use Manager - required if MU attestation is required
- Super-Users - early adopters for training programs
The makeup of your implementation team will depend on the scope of your practice, budget… and project manager’s patience. A key decision to make at this stage is whether to bring in external EHR implementation specialists or consultants…
What does an EHR implementation specialist do?
"Things senior practice management will ask when presented with the bill."
The answer is everything. And, potentially, nothing. It’s not the abilities of an EHR consultant that matter, it’s how you use them to assist with any combination of...
- Project scheduling and roadmapping
- Data migration and cleansing
- User training and change management
- Testing and go-live activities
- Security assessment
...just don’t put them solely in charge of the budget (their paycheck).
3. Forecast your EHR implementation costs and define a budget
Now you have a team and a to-do list, you are in a position to ask…
What is the cost of EHR implementation?
The only answer one can give with some certainty at this stage is…
… approximately $6,000 more than you expected.
Having said that, a well-defined budget featuring the following elements should ensure no unexpected costs come out of the woodwork:
- Hardware and network upgrades
- Practice staff overtime and temporary staff
- Productivity loss (some estimate as high as 50% reductions in patient throughput)
- Customization consultancy from the EHR vendor
- Vendor training fees
- Consultancy costs
- Data backups and storage (often bundled with cloud EHR costs)
A recent EHR report found that most practices can expect to spend around $6,200 per user of their software, so bear this figure in mind, in hand with the elements above, when considering your projected budget.
If you're looking for information on the upfront cost of purchasing EHR software, you can download our EHR software pricing guide here.
4. Schedule your EHR implementation
This is often the first thing practices work on. The problem with that approach is clear when you consider what impacts a schedule:
- Project scope
- Project teams
- Project budgets
Luckily for you, you have now defined all three and can begin to add timescales to your roadmap outlined in step one. So the question is:
How long does an EHR implementation take?
611 hours is the simple answer.
The complicated answer is an analysis of our holy trinity of project attributes outlined above.
5. Migration of patient data and practice data
This is the point where the everyone has to keep their nose to the grindstone. Or their cleansed patient data to the well-formatted EHR database if you want to be literal.
Key stages in EHR data migration include:
- Conversion of paper records to electronic records
- Data cleansing and verification
- EHR database setup
- Mapping legacy data to new database fields
- Data transfer to the new system
- Testing and verification of legacy data
- Testing and verification of new data inputs
Get this process right and the rewards are great… a 10% reduction in data errors to be precise.
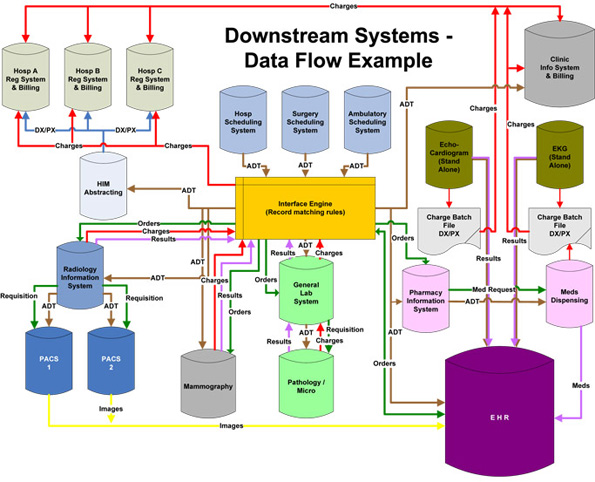
To clarify this process, it is useful to produce a map of your practice data as shown above (source: Advance Healthcare Network)
6. Create a use training program
With $70,000 in annual savings and a 10% increase in productivity at stake, your EHR training program has a huge impact on the final ROI for your system.
Successful training programs include:
- Super-users as system and program advocates
- Clear communication channels with vendor support teams
- Role-based training to ensure relevancy
- Feedback loops to keep users in dialogue with project management
These steps should not be seen as silver bullets as one of the primary causes of EHR implementation failure is poor user adoption of the system.
7. Clearly define go-live activities
If there is ever a day to have a plan it is go-live day. Day one. The start of the rest of your life.
With that in mind, it is prudent to create a zoomed in version of your roadmap specifically for the days (or weeks) around your go-live date. This roadmap can include:
- System testing processes (pre- and post-go-live)
- Patient communication guidelines (including expected downtime)
- Staff scheduling including required overtime or temporary staff
- Modification of appointments and scheduling
- Reporting processes for system and project evaluation (see step 8)
- In-practice communications (signs on noticeboards etc.)
- Network speed and reliability checks
- Data backup processes
8. Define critical success factors and evaluation strategies
Congratulations, you made it through go-live. Or at the very least the planning process.
Now you should ask…
How can you evaluate your EHR implementation?
Evaluation of EHR implementation can take many forms and the best one for your practice will depend on your project goals:
- Perform ROI calculations to assess profitability
- Record patient throughput to assess efficiency
- Survey patient satisfaction to assess quality of care
- Survey physician satisfaction to assess user adoption and training
- Analyse data error rates to assess data input and quality
A final thought…
Following these steps will produce a plan which gives your project a foundation. It is up to you and your team to execute this plan in the face of practice nuances, disgruntled users and missing data (even the best implementations experience these).
Free white paper

EHR implementation: 6 steps to success
Step-by-step information on how to implement EHR effectively

Featured white papers
-

EHR Implementation Template
Get all the planning tools you need to make your EHR implementation a success
Download -

EHR implementation: 6 steps to success
Step-by-step information on how to implement EHR effectively
Download -

EHR Vendor Directory
Get the most up-to-date directory of EHR software vendors. Find the best software for your practice.
Download
Related articles
-

How much EHR costs and how to set your budget
Build a realistic, workable budget for your EHR project with this guide
-

A template for your EHR project implementation timeline
Determining your EHR project timeline will prove tricky, but having some expectations of time fra...
-

5 important areas of EHR training during implementation
Successful EHR implementation is not possible without crucial EHR training

